diff --git a/docs/public/AGENTS.md b/docs/public/AGENTS.md
index 2352e36c..ef4306bf 100644
--- a/docs/public/AGENTS.md
+++ b/docs/public/AGENTS.md
@@ -12,34 +12,34 @@
## 1. Positioning and Capability Boundaries
-- **What**: Lynx is a cross-platform rendering engine that treats the web as its semantic baseline. It targets iOS, Android, HarmonyOS, and the web with a single codebase. A unified element abstraction maps to native views or custom web elements on different hosts, avoiding the performance bottlenecks of traditional WebViews. (See [Composing Elements](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/elements-components.md))
-- **Why**: Mobile users are extremely sensitive to first-screen time and interaction latency. Lynx combines a dual-thread JavaScript runtime, Instant First-Frame Rendering (IFR), and a native rendering pipeline to deliver the React developer experience alongside near-native performance. (See [Instant First-Frame Rendering](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
-- **How**: On the tooling side, use Rspeedy (an Rspack-powered build tool) to generate a Lynx bundle. On the front end, ReactLynx (a React implementation with a Preact core) describes the UI and communicates with the host through Native Modules or Custom Elements. (See [ReactLynx](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/introduction.md), [Native Modules](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/use-native-modules.md))
+- **What**: Lynx is a cross-platform rendering engine that treats the web as its semantic baseline. It targets iOS, Android, HarmonyOS, and the web with a single codebase. A unified element abstraction maps to native views or custom web elements on different hosts, avoiding the performance bottlenecks of traditional WebViews. (See [Composing Elements](/guide/ui/elements-components.md))
+- **Why**: Mobile users are extremely sensitive to first-screen time and interaction latency. Lynx combines a dual-thread JavaScript runtime, Instant First-Frame Rendering (IFR), and a native rendering pipeline to deliver the React developer experience alongside near-native performance. (See [Instant First-Frame Rendering](/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
+- **How**: On the tooling side, use Rspeedy (an Rspack-powered build tool) to generate a Lynx bundle. On the front end, ReactLynx (a React implementation with a Preact core) describes the UI and communicates with the host through Native Modules or Custom Elements. (See [ReactLynx](/react/introduction.md), [Native Modules](/guide/use-native-modules.md))
## 2. Mental Model: Align Lynx with the Web
-| Web Mental Model | Lynx Counterpart | Key Differences |
-| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| `index.html` + assets | Lynx bundle (binary that contains JS bytecode + styles) or a `template.js` file | Bundles must be compatible with the Lynx engine version; configure `engineVersion` (previously `targetSdkVersion`). (See [Compatibility](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/compatibility.md)) |
-| DOM + CSSOM | Element tree + styling system | Every element behaves like a block-level node. Custom tags such as `view`/`text` map to native controls. (See [Composing Elements](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/elements-components.md)) |
-| Browser main thread | Lynx main thread | Handles first-screen rendering, layout, and main-thread scripts, executing PrimJS bytecode. (See [Main Thread Runtime](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/scripting-runtime/main-thread-runtime.md)) |
-| Browser rendering-task queue | Lynx background thread | Runs ReactLynx scheduling, lifecycle, and most side effects. Executes PrimJS/JavaScriptCore with syntax support up to ES2015 (SWC transpiles during build). (See [JavaScript Runtime](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md)) |
-| `window` / `document` | `lynx` global object + API set | No DOM APIs. Access nodes via `lynx.getElementById`, SelectorQuery, `main-thread:ref`, etc. (See [ReactLynx](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/introduction.md), [Direct Manipulation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md)) |
+| Web Mental Model | Lynx Counterpart | Key Differences |
+| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.html` + assets | Lynx bundle (binary that contains JS bytecode + styles) or a `template.js` file | Bundles must be compatible with the Lynx engine version; configure `engineVersion` (previously `targetSdkVersion`). (See [Compatibility](/guide/compatibility.md)) |
+| DOM + CSSOM | Element tree + styling system | Every element behaves like a block-level node. Custom tags such as `view`/`text` map to native controls. (See [Composing Elements](/guide/ui/elements-components.md)) |
+| Browser main thread | Lynx main thread | Handles first-screen rendering, layout, and main-thread scripts, executing PrimJS bytecode. (See [Main Thread Runtime](/guide/scripting-runtime/main-thread-runtime.md)) |
+| Browser rendering-task queue | Lynx background thread | Runs ReactLynx scheduling, lifecycle, and most side effects. Executes PrimJS/JavaScriptCore with syntax support up to ES2015 (SWC transpiles during build). (See [JavaScript Runtime](/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md)) |
+| `window` / `document` | `lynx` global object + API set | No DOM APIs. Access nodes via `lynx.getElementById`, SelectorQuery, `main-thread:ref`, etc. (See [ReactLynx](/react/introduction.md), [Direct Manipulation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md)) |
## 3. Runtime Architecture: How Dual-Thread React Works
-- **Dual-thread parallel rendering**: The main thread renders ReactLynx output immediately for the first screen, while the background thread constructs the full node tree and syncs state back to the main thread to avoid a white screen. (See [Rendering Process and Lifecycle](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/lifecycle.md), [IFR](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
+- **Dual-thread parallel rendering**: The main thread renders ReactLynx output immediately for the first screen, while the background thread constructs the full node tree and syncs state back to the main thread to avoid a white screen. (See [Rendering Process and Lifecycle](/react/lifecycle.md), [IFR](/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
- **“Your code runs on two threads”**: Dual-thread React means your logic can run on both threads. However, not all code can execute in both environments—some APIs are only available on the background thread, and ReactLynx only executes events, lifecycle hooks, and `useEffect`-style side effects from the background thread.
- **`'background only'`**: Any function that does not need to run on the main thread (for example event handlers, lifecycle hooks, side effects) or that touches background-only APIs must add `'background only'` as the first statement. Modules can declare `import "background-only"` to indicate they expect to run exclusively on the background thread.
-- **Main Thread Script (MTS)**: Functions marked with the `'main thread';` directive run directly on the main thread, ideal for high-frequency gestures, animations, and zero-delay feedback. Main-thread events must use the `main-thread:` prefix (for example `main-thread:bindtap`, `useMainThreadRef`). (See [Main Thread Script](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/main-thread-script.md))
+- **Main Thread Script (MTS)**: Functions marked with the `'main thread';` directive run directly on the main thread, ideal for high-frequency gestures, animations, and zero-delay feedback. Main-thread events must use the `main-thread:` prefix (for example `main-thread:bindtap`, `useMainThreadRef`). (See [Main Thread Script](/react/main-thread-script.md))
- **Cross-thread communication**: Use `runOnMainThread` and `runOnBackground` for asynchronous cross-thread calls. Arguments must be JSON-serializable.
## 4. UI Construction: Element System and Native Mapping
-- **Element tags**: Built-in tags such as `view`, `text`, `image`, `scroll-view`, etc. abstract native controls. They are not DOM nodes, but the syntax (start/end tag, attributes) stays HTML-like. (See [Composing Elements](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/elements-components.md))
+- **Element tags**: Built-in tags such as `view`, `text`, `image`, `scroll-view`, etc. abstract native controls. They are not DOM nodes, but the syntax (start/end tag, attributes) stays HTML-like. (See [Composing Elements](/guide/ui/elements-components.md))
- **Cross-platform mapping**: The same element automatically maps to the platform’s native view (`view` → iOS `UIView`, Android `ViewGroup`; on the web it becomes a custom element), so you do not need platform-specific code.
-- **Text semantics**: Text must live inside the `text` element. You cannot drop plain text inside a `div` equivalent. Inline layout relies on nested `text` elements. (See [Typography](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/styling/text-and-typography.md))
-- **Extensibility**: When the built-in set is not enough, register custom native elements. Implement them per platform (iOS/Android/Harmony) and use them through a unified tag. (See [Custom Element](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/custom-native-component.md))
+- **Text semantics**: Text must live inside the `text` element. You cannot drop plain text inside a `div` equivalent. Inline layout relies on nested `text` elements. (See [Typography](/guide/styling/text-and-typography.md))
+- **Extensibility**: When the built-in set is not enough, register custom native elements. Implement them per platform (iOS/Android/Harmony) and use them through a unified tag. (See [Custom Element](/guide/custom-native-component.md))
Additionally:
@@ -47,17 +47,17 @@ Additionally:
## 5. Layout System: Block by Default with Four Layout Modes
-| Layout mode | Web counterpart | Lynx-specific notes |
-| ------------------- | -------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| `display: linear` | No direct counterpart; simplified flex-like layout | The main axis is vertical by default. Use `linear-direction` and `linear-weight` to distribute space—suited for linear arrangements. (See [Linear Layout](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/layout/linear-layout.md)) |
-| `display: flex` | CSS Flexbox | Most properties match CSS, but `min-content` is unsupported and the shrink lower bound is treated as `0px`. (See [Flexible Box Layout](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/layout/flexible-box-layout.md)) |
-| `display: grid` | CSS Grid | Supports common row/column definitions and gaps; currently lacks `grid-area` and line names. (See [Grid Layout](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/layout/grid-layout.md)) |
-| `display: relative` | Android RelativeLayout mental model | Effective on mobile only. Use `relative-*` properties to describe positioning relative to siblings/parent. (See [Relative Layout](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/layout/relative-layout.md)) |
+| Layout mode | Web counterpart | Lynx-specific notes |
+| ------------------- | -------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `display: linear` | No direct counterpart; simplified flex-like layout | The main axis is vertical by default. Use `linear-direction` and `linear-weight` to distribute space—suited for linear arrangements. (See [Linear Layout](/guide/ui/layout/linear-layout.md)) |
+| `display: flex` | CSS Flexbox | Most properties match CSS, but `min-content` is unsupported and the shrink lower bound is treated as `0px`. (See [Flexible Box Layout](/guide/ui/layout/flexible-box-layout.md)) |
+| `display: grid` | CSS Grid | Supports common row/column definitions and gaps; currently lacks `grid-area` and line names. (See [Grid Layout](/guide/ui/layout/grid-layout.md)) |
+| `display: relative` | Android RelativeLayout mental model | Effective on mobile only. Use `relative-*` properties to describe positioning relative to siblings/parent. (See [Relative Layout](/guide/ui/layout/relative-layout.md)) |
Additionally:
-- Every element defaults to `box-sizing: border-box`; margin collapsing does not occur. (See [Understanding Layout](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/layout/index.md))
-- There is no `inline` vs. `block` toggle; text layout relies on the `text` element. (See [Typography](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/styling/text-and-typography.md))
+- Every element defaults to `box-sizing: border-box`; margin collapsing does not occur. (See [Understanding Layout](/guide/ui/layout/index.md))
+- There is no `inline` vs. `block` toggle; text layout relies on the `text` element. (See [Typography](/guide/styling/text-and-typography.md))
- Logical directions (such as `inline-start`) depend on `direction` and require CSS inheritance to be enabled.
- `overflow: scroll` is unsupported. Use `` and enable scrolling with either the `scroll-y` or `scroll-x` attribute.
- `position` supports `relative`, `absolute`, and `fixed`. Nodes with `fixed` are promoted directly under the root node.
@@ -65,38 +65,38 @@ Additionally:
## 6. Styling System: CSS Syntax with Lynx Configuration
- **Special units**: Supports the `rpx` unit to adapt to different screen sizes.
-- **Selectors and inline styles**: Largely identical to the web. Combine with PostCSS/Sass nesting if needed. (See [Styling with CSS](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/styling.md))
-- **Extended properties**: `-x-` prefixed properties expose mobile capabilities such as `-x-auto-font-size`. (See [Styling with CSS](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/ui/styling.md))
-- **Theming and inheritance**: CSS variables and class switching are supported. Regular properties do not inherit by default—enable `enableCSSInheritance` in `pluginReactLynx` or configure `customCSSInheritanceList`. (See [Custom properties (`--*`): CSS variables](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/css/properties/css-variable.md), [Theming](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/styling/custom-theming.md))
+- **Selectors and inline styles**: Largely identical to the web. Combine with PostCSS/Sass nesting if needed. (See [Styling with CSS](/guide/ui/styling.md))
+- **Extended properties**: `-x-` prefixed properties expose mobile capabilities such as `-x-auto-font-size`. (See [Styling with CSS](/guide/ui/styling.md))
+- **Theming and inheritance**: CSS variables and class switching are supported. Regular properties do not inherit by default—enable `enableCSSInheritance` in `pluginReactLynx` or configure `customCSSInheritanceList`. (See [Custom properties (`--*`): CSS variables](/api/css/properties/css-variable.md), [Theming](/guide/styling/custom-theming.md))
- **Fonts**: Supports `@font-face` and `lynx.addFont`, but the host must implement font loading.
## 7. ReactLynx: Familiar APIs with Lynx Constraints
-- **API parity**: Almost identical to React; `import { useState } from '@lynx-js/react'`. The runtime is powered by Preact. (See [What is ReactLynx](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/introduction.md))
-- **Lifecycle**: All lifecycle hooks run asynchronously on the background thread. `useLayoutEffect` is disabled; use `main-thread:bindlayoutchange` to obtain layout information and update properties instead. (See [Rendering Process and Lifecycle](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/lifecycle.md))
+- **API parity**: Almost identical to React; `import { useState } from '@lynx-js/react'`. The runtime is powered by Preact. (See [What is ReactLynx](/react/introduction.md))
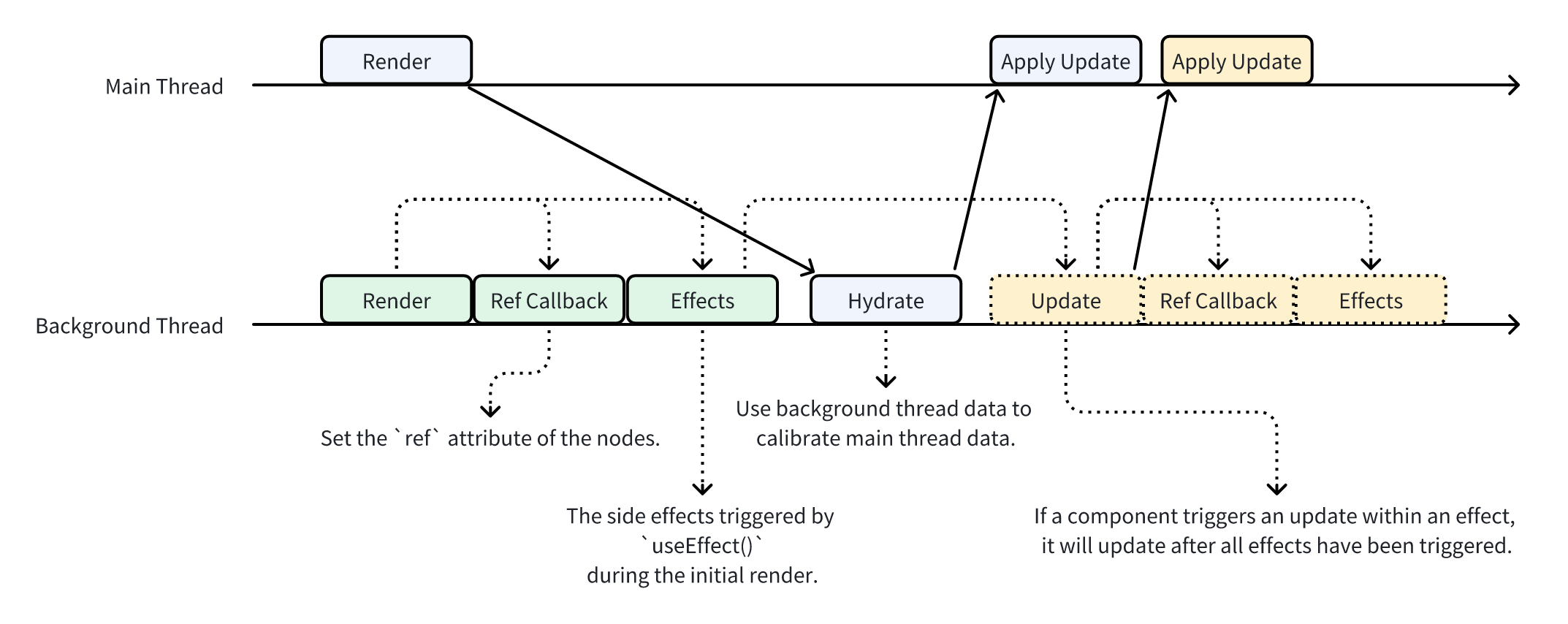
+- **Lifecycle**: All lifecycle hooks run asynchronously on the background thread. `useLayoutEffect` is disabled; use `main-thread:bindlayoutchange` to obtain layout information and update properties instead. (See [Rendering Process and Lifecycle](/react/lifecycle.md))
-- **Background-only restrictions**: The framework can statically infer some direct cases, but once indirection is introduced—passing event handlers through components or writing custom hooks—you must explicitly add the `'background only'` directive. (See [Thinking in ReactLynx](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/thinking-in-reactlynx.md))
+- **Background-only restrictions**: The framework can statically infer some direct cases, but once indirection is introduced—passing event handlers through components or writing custom hooks—you must explicitly add the `'background only'` directive. (See [Thinking in ReactLynx](/react/thinking-in-reactlynx.md))
- **Main-thread functions**: Add `'main thread';` at the top of the function body. Such functions can only run on the main thread (for example in event handlers or `main-thread:ref`). Captured outer variables are snapshotted and must be JSON-serializable, so you cannot capture functions directly.
- **Cross-thread execution**: You cannot call a function defined on the other thread directly. Use `runOnMainThread` / `runOnBackground`, which return Promises for cross-thread calls.
-- **Module system**: ESM and CommonJS are both supported and can be mixed, though ESM is recommended. Rspeedy/SWC handles module transformation during the build. (See [JavaScript Runtime](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md))
+- **Module system**: ESM and CommonJS are both supported and can be mixed, though ESM is recommended. Rspeedy/SWC handles module transformation during the build. (See [JavaScript Runtime](/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md))
## 8. Type System
-- **TypeScript support**: Official typings live in `@lynx-js/types`; using TypeScript throughout is highly encouraged. (See [TypeScript Support](https://lynxjs.org/next/rspeedy/typescript))
+- **TypeScript support**: Official typings live in `@lynx-js/types`; using TypeScript throughout is highly encouraged. (See [TypeScript Support](/rspeedy/typescript))
- **`tsconfig.json`**: Set `compilerOptions.jsx` to `react-jsx` and `compilerOptions.jsxImportSource` to `@lynx-js/react`.
- **Import types correctly**: All Lynx API types are exported from `@lynx-js/types`, for example `import type { MainThread, NodesRef } from '@lynx-js/types'`. ReactLynx APIs and types come from `@lynx-js/react`.
## 9. Event Model: Naming and Propagation
-- **Event attribute names**: `bindtap`, `catchtap`, `capture-bindtap`, `global-bindtap`, etc. denote phase/interception. Main-thread events require the `main-thread:` prefix. (See [Event Propagation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/event-propagation.md))
+- **Event attribute names**: `bindtap`, `catchtap`, `capture-bindtap`, `global-bindtap`, etc. denote phase/interception. Main-thread events require the `main-thread:` prefix. (See [Event Propagation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/event-propagation.md))
- **Propagation phases**: Capture plus bubble over the element tree path. Non-touch events fire only on the target node.
-- **Event object differences**: The background thread receives plain JSON. Main-thread events expose `MainThread.Element` through `currentTarget`, allowing direct node operations (such as `setStyleProperty`). (See [Event Handling](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling.md))
-- **Global events**: `GlobalEventEmitter` supports cross-component and host broadcasts and must be used on the background thread. (See [Event Propagation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/event-propagation.md))
+- **Event object differences**: The background thread receives plain JSON. Main-thread events expose `MainThread.Element` through `currentTarget`, allowing direct node operations (such as `setStyleProperty`). (See [Event Handling](/guide/interaction/event-handling.md))
+- **Global events**: `GlobalEventEmitter` supports cross-component and host broadcasts and must be used on the background thread. (See [Event Propagation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/event-propagation.md))
- **AOP interception**: `lynx.beforePublishEvent` lets you intercept events centrally on the background thread.
## 10. Node References and Direct Manipulation
-- **Background thread**: Use `useRef` with `ref={...}` and operate via `invoke()` / `setNativeProps()`. Remember to call `.exec()` at the end to submit batched operations. (See [Direct Manipulation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
+- **Background thread**: Use `useRef` with `ref={...}` and operate via `invoke()` / `setNativeProps()`. Remember to call `.exec()` at the end to submit batched operations. (See [Direct Manipulation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
- **Main thread**: `useMainThreadRef` plus `main-thread:ref` yields `MainThread.Element`, which exposes methods such as `setStyleProperty` and `invoke`.
- **Selector APIs**: On the background thread, `lynx.createSelectorQuery()` produces `NodesRef`. On the main thread, use `lynx.querySelector()` / `lynx.querySelectorAll()` to obtain `MainThread.Element`.
- **Getting the event target**: Background-thread event payloads do not carry node references. On the main thread, `event.currentTarget` is a `MainThread.Element`.
@@ -106,52 +106,52 @@ Case study:
- **Retrieve layout information**: Choose the approach that fits your scenario:
- Via events: Listen to `bindlayoutchange` for layout updates—the event object contains layout data. With Main Thread Script, use the main-thread variant `main-thread:bindlayoutchange`.
- - Direct node access: Call `boundingClientRect` on the node. Background thread uses `NodesRef.invoke`; main thread uses `MainThread.Element.invoke`. (See [Direct Manipulation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
+ - Direct node access: Call `boundingClientRect` on the node. Background thread uses `NodesRef.invoke`; main thread uses `MainThread.Element.invoke`. (See [Direct Manipulation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
Common APIs:
-- [Interface `NodesRef`](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref.md)
-- [invoke()](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref/nodes-ref-invoke.md)
-- [setNativeProps()](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref/nodes-ref-set-native-props.md)
-- [Interface `MainThread.Element`](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/main-thread/main-thread-element.md)
-- [animate()](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/main-thread/lynx-animate-api.md)
-- [Interface `SelectorQuery`](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/selector-query.md)
-- [exec()](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/selector-query/selector-query-exec.md)
-- [select()](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/lynx-api/selector-query/selector-query-select.md)
+- [Interface `NodesRef`](/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref.md)
+- [invoke()](/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref/nodes-ref-invoke.md)
+- [setNativeProps()](/api/lynx-api/nodes-ref/nodes-ref-set-native-props.md)
+- [Interface `MainThread.Element`](/api/lynx-api/main-thread/main-thread-element.md)
+- [animate()](/api/lynx-api/main-thread/lynx-animate-api.md)
+- [Interface `SelectorQuery`](/api/lynx-api/selector-query.md)
+- [exec()](/api/lynx-api/selector-query/selector-query-exec.md)
+- [select()](/api/lynx-api/selector-query/selector-query-select.md)
## 11. Data Input and Host Communication
-- **Init data**: The host injects initial data with `LynxView.loadTemplate`. Front-end code accesses it via `useInitData`; updates trigger automatic re-rendering. (See [Using Data from Host Platform](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/use-data-from-host-platform.md))
+- **Init data**: The host injects initial data with `LynxView.loadTemplate`. Front-end code accesses it via `useInitData`; updates trigger automatic re-rendering. (See [Using Data from Host Platform](/guide/use-data-from-host-platform.md))
- **Data processors**: Use `lynx.registerDataProcessors` to normalize multi-end data structures with named processors on the front end.
- **Global properties**: Read host configurations (such as dark mode) from `lynx.__globalProps` and pair them with theme switching. Actual properties are host-defined; if the host does not provide them, `lynx.__globalProps` is `null` or an empty object.
-- **Guaranteeing IFR**: As long as initial data arrives synchronously and the Lynx bundle loads synchronously, the main thread can render a first frame with no white screen. (See [IFR](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
+- **Guaranteeing IFR**: As long as initial data arrives synchronously and the Lynx bundle loads synchronously, the main thread can render a first frame with no white screen. (See [IFR](/guide/interaction/ifr.md))
## 12. Extending Host Capabilities
-- **Native Modules**: Declare TypeScript types, implement them separately on iOS/Android/Harmony, and register them. Front-end code calls `NativeModules.xxx` on the background thread. (See [Native Modules](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/use-native-modules.md))
-- **Custom elements**: When you need capabilities closer to native controls (for example customized inputs), extend `LynxUI` on the host, implement attributes/events/commands, and use it just like a built-in element. (See [Custom Element](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/custom-native-component.md))
+- **Native Modules**: Declare TypeScript types, implement them separately on iOS/Android/Harmony, and register them. Front-end code calls `NativeModules.xxx` on the background thread. (See [Native Modules](/guide/use-native-modules.md))
+- **Custom elements**: When you need capabilities closer to native controls (for example customized inputs), extend `LynxUI` on the host, implement attributes/events/commands, and use it just like a built-in element. (See [Custom Element](/guide/custom-native-component.md))
- **SelectorQuery invoking native commands**: Call `invoke({ method: 'focus' })` to trigger native methods exposed by custom elements. Consult the element’s documentation for supported commands.
## 13. Networking and Runtime Differences
-- **Fetch API**: The interface aligns with the web, but depends on the host-provided HTTP service. Enable streaming responses via `lynxExtension.useStreaming` and read from `response.body`. Review official compatibility notes as needed. (See [Networking](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/networking.md))
-- **Encoding helpers**: PrimJS currently lacks `TextEncoder` / `TextDecoder`, so use `TextCodecHelper` for UTF-8 encoding/decoding. (See [Networking](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/networking.md))
-- **Global object limitations**: There is no `window` or `document`. Replace browser APIs with `lynx` alternatives (such as `lynx.reload`). (See [ReactLynx](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/introduction.md))
-- **Polyfills and syntax**: PrimJS on the main thread supports up to ES2019; the background thread supports ES2015. The build injects polyfills automatically (primarily for iOS). (See [JavaScript Runtime](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md))
+- **Fetch API**: The interface aligns with the web, but depends on the host-provided HTTP service. Enable streaming responses via `lynxExtension.useStreaming` and read from `response.body`. Review official compatibility notes as needed. (See [Networking](/guide/interaction/networking.md))
+- **Encoding helpers**: PrimJS currently lacks `TextEncoder` / `TextDecoder`, so use `TextCodecHelper` for UTF-8 encoding/decoding. (See [Networking](/guide/interaction/networking.md))
+- **Global object limitations**: There is no `window` or `document`. Replace browser APIs with `lynx` alternatives (such as `lynx.reload`). (See [ReactLynx](/react/introduction.md))
+- **Polyfills and syntax**: PrimJS on the main thread supports up to ES2019; the background thread supports ES2015. The build injects polyfills automatically (primarily for iOS). (See [JavaScript Runtime](/guide/scripting-runtime/index.md))
## 14. Performance Tooling and Tuning
-- **Main Thread Script**: Keep animations/gestures responsive while respecting thread isolation and data synchronization. (See [Main Thread Script](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/main-thread-script.md))
-- **NodesRef.invoke**: Batch native operations (for example `autoScroll`) to avoid cross-thread overhead. (See [Direct Manipulation](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
-- **Lynx DevTool & Trace**: The desktop DevTool offers Elements/Console/Sources/Trace panels to record render pipelines and analyze the ReactLynx render process. (See [Lynx DevTool](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/devtool.md), [Trace](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/devtool/trace.md))
-- **Performance metrics**: Use `lynx.performance` and `PerformanceObserver` to capture metrics such as FCP and InitContainer. (See [Performance API](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/performance/metrics/performance-api.md))
+- **Main Thread Script**: Keep animations/gestures responsive while respecting thread isolation and data synchronization. (See [Main Thread Script](/react/main-thread-script.md))
+- **NodesRef.invoke**: Batch native operations (for example `autoScroll`) to avoid cross-thread overhead. (See [Direct Manipulation](/guide/interaction/event-handling/manipulating-element.react.md))
+- **Lynx DevTool & Trace**: The desktop DevTool offers Elements/Console/Sources/Trace panels to record render pipelines and analyze the ReactLynx render process. (See [Lynx DevTool](/guide/devtool.md), [Trace](/guide/devtool/trace.md))
+- **Performance metrics**: Use `lynx.performance` and `PerformanceObserver` to capture metrics such as FCP and InitContainer. (See [Performance API](/guide/performance/metrics/performance-api.md))
## 15. Engineering Practices and Tooling
-- **Project initialization**: `pnpm create rspeedy` scaffolds a ReactLynx project with Rspeedy configuration and sample code. (See [Quick Start](https://lynxjs.org/next/rspeedy/start/quick-start.md))
-- **Development and debugging**: `pnpm dev` starts the Rspeedy dev server. The terminal prints a QR code—scan it with the LynxExample app (iOS/Android/Harmony emulator) for hot-update previews. (See [Quick Start](https://lynxjs.org/next/rspeedy/start/quick-start.md))
-- **DevTool debugging**: After connecting a device, use the desktop Lynx DevTool to debug JS, inspect nodes, and record performance. (See [Lynx DevTool](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/devtool.md))
-- **Build artifacts**: Rspeedy outputs a bundle that includes the background-thread script (text), main-thread bytecode, styles, and other assets. Set `DEBUG=rspeedy` to dump intermediate artifacts (background script, main-thread bytecode, styles, source maps, etc.) into `dist/.rspeedy`; otherwise only the final bundle is produced. (See [Output Files](https://lynxjs.org/next/rspeedy/output.md))
+- **Project initialization**: `pnpm create rspeedy` scaffolds a ReactLynx project with Rspeedy configuration and sample code. (See [Quick Start](/rspeedy/start/quick-start.md))
+- **Development and debugging**: `pnpm dev` starts the Rspeedy dev server. The terminal prints a QR code—scan it with the LynxExample app (iOS/Android/Harmony emulator) for hot-update previews. (See [Quick Start](/rspeedy/start/quick-start.md))
+- **DevTool debugging**: After connecting a device, use the desktop Lynx DevTool to debug JS, inspect nodes, and record performance. (See [Lynx DevTool](/guide/devtool.md))
+- **Build artifacts**: Rspeedy outputs a bundle that includes the background-thread script (text), main-thread bytecode, styles, and other assets. Set `DEBUG=rspeedy` to dump intermediate artifacts (background script, main-thread bytecode, styles, source maps, etc.) into `dist/.rspeedy`; otherwise only the final bundle is produced. (See [Output Files](/rspeedy/output.md))
## 16. Key Differences from the Web
@@ -196,29 +196,29 @@ Common APIs:
The following official Lynx tutorials cover scenarios from beginner to advanced—work through them hands-on:
-- Product gallery — build a two-column product page step by step: [Tutorial Gallery](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/start/tutorial-gallery.md). You will learn to:
+- Product gallery — build a two-column product page step by step: [Tutorial Gallery](/guide/start/tutorial-gallery.md). You will learn to:
- Build foundational UI with styling and interactions
- Componentize the layout
- Render high-performance long lists with the `` element
- Manipulate nodes directly via `NodesRef.invoke` to implement auto-scrolling
- - Customize scrollbars and leverage [Main Thread Script](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/main-thread-script.md) to optimize scrolling performance
-- Product detail — implement a carousel component to practice high-performance interaction code: [Tutorial Product Detail](https://lynxjs.org/next/guide/start/tutorial-product-detail.md). You will learn to:
+ - Customize scrollbars and leverage [Main Thread Script](/react/main-thread-script.md) to optimize scrolling performance
+- Product detail — implement a carousel component to practice high-performance interaction code: [Tutorial Product Detail](/guide/start/tutorial-product-detail.md). You will learn to:
- Manipulate nodes directly with `NodesRef.setNativeProps` to update styles and attributes
- - Use [Main Thread Script](https://lynxjs.org/next/react/main-thread-script.md) to reduce latency
+ - Use [Main Thread Script](/react/main-thread-script.md) to reduce latency
- Call between main-thread and background-thread functions
- Pass values between main-thread and background-thread scripts
## 20. Appendix: Key Built-in Elements
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/view.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/text.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/image.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/scroll-view.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/list.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/page.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/frame.md)
-- [`` element](https://lynxjs.org/next/api/elements/built-in/input.md)
-- [`