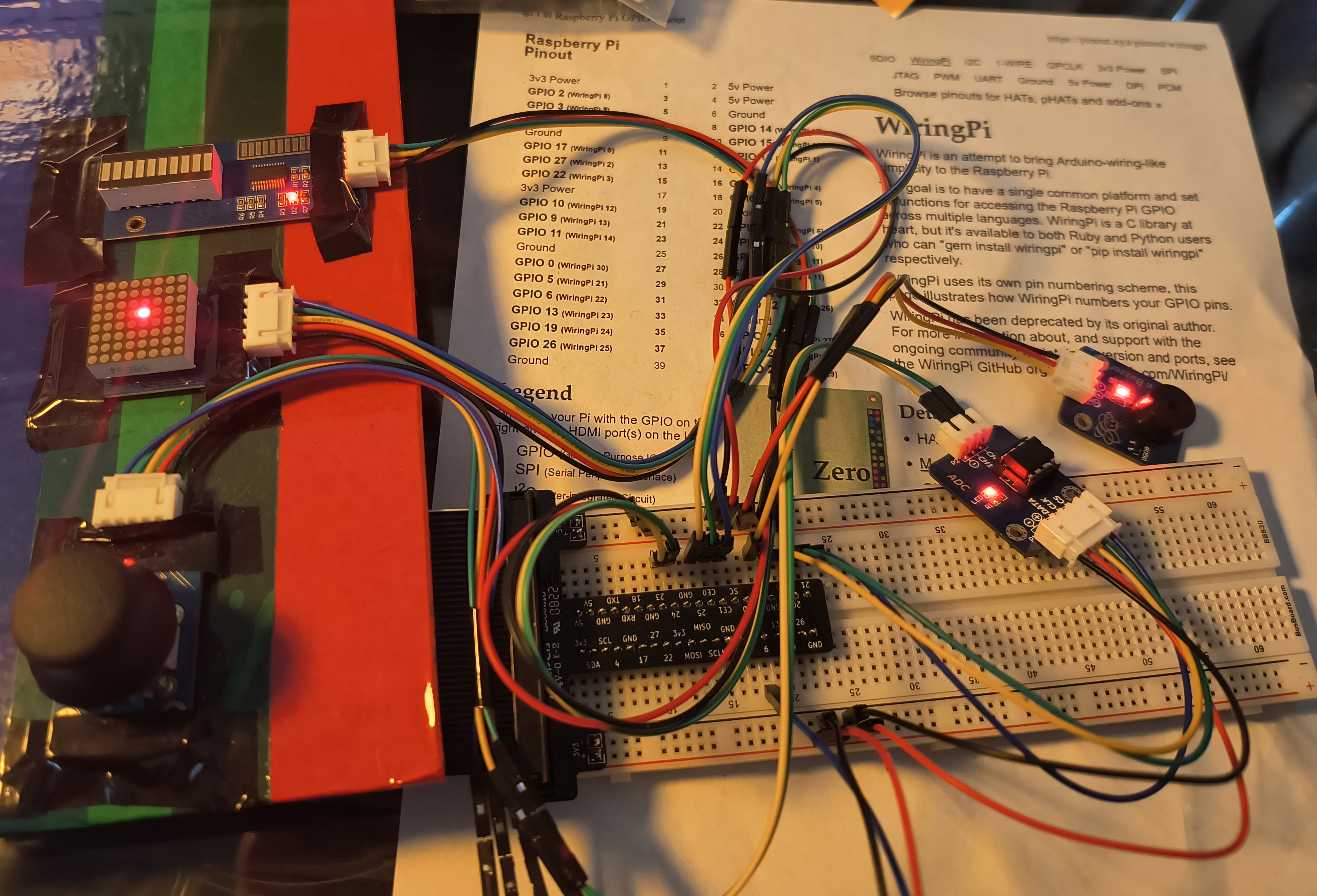
A Raspberry Pi controlled Simon-inspired pattern game. Match the directions in the correct sequence to continue to the next level.
Created by Miles Murgaw as a final project for CNIT 105 @ Purdue Polytechnic.
- 8x8 LED Matrix for displaying directions, and other effects. Main display.
- LED Bar for displaying current level.
- Passive buzzer for audio effects and tunes.
- XY + Z Button Joystick for matching patterns. Primary input.
This project is organized into a handful of files.
main.ccontains the main game logic and control flow.led_matrix.ccontains the led matrix rendering logic.led_bar.ccontains the led bar rendering logic.buzzer.ccontains the tunes and audio effect logic.joystick.ccontains the logic to read joystick input, including a bit-banged protocol implementation for the ADC ADC0832.
The program runs in only two threads: the main game thread, and a secondary thread for rendering the LED matrix.
Below is the described step-by-step program flow.
- Upon startup, peripherals are initialized, including the matrix LED which spawns the render thread.
- The program will start the core loop which handles starting the game when the user is ready.
- If the joystick button is pressed, the game will start.
The LED Matrix can only enable individual LEDs at a time, and in order to display pictures, we must quickly loop through and turn on and off the individual leds that each frame requires, creating the illusion of a picture.
During initialization, the LED matrix spawns a new thread who's sole job is to continiously render the currently selected frame. This allows the main game thread to continue executing without being blocked or limited by the LED matrix render thread.
The game is organized into a single infinite while loop.
- A new pattern will be chosen at random and added to the list of patterns to match. The pattern will be briefly displayed to the user.
- A new loops runs until the number of inputs matches the total number of patterns to match. If the user incorrectly matches a pattern, the loop exits and indicates a failed state.
- If the previous loop indicated a fail state, the game will indicate that the user lost, and will exit the core game loop.
- If the user succeeded in matching all patterns, the level will increase and the game loop will repeat.
Each file contains it's required pin definitions used by the wiringPi library. Each device has it's own PWR and GND, all connected to 5V, other than the joystick and ADC which uses 3.3V.
The joystick uses an ADC for the analog inputs.
| Breakout Pin | RPI GPIO | ADC |
|---|---|---|
| Y | N/A | CH1 |
| X | N/A | CH0 |
| Z | GPIO 06 | N/A |
The ADC is used to read analog joystick signals.
| Breakout Pin | RPI GPIO |
|---|---|
| DATA | GPIO 16 |
| CLK | GPIO 20 |
| CS | GPIO 21 |
| Breakout Pin | RPI GPIO |
|---|---|
| ST_CP | GPIO 25 |
| SH_CP | GPIO 08 |
| DS | GPIO 07 |
| Breakout Pin | RPI GPIO |
|---|---|
| DCKI | GPIO 23 |
| DI | GPIO 24 |
| Breakout Pin | RPI GPIO |
|---|---|
| S | GPIO 12 |
This project is meant to be compiled on a Raspberry Pi. This has only been tested on an RPI 4B.
Debug:
gcc src/main.c src/led_matrix.c src/led_bar.c src/buzzer.c src/joystick.c -o game -lwiringPi -lpthreadRelease:
gcc src/main.c src/led_matrix.c src/led_bar.c src/buzzer.c src/joystick.c -o game -lwiringPi -lpthread -O3 -DNDEBUG -march=native -mtune=native