A cross platform (Windows/Linux/etc) Least Frequently Used (LFU) Cache implementation in .NET that evicts items based on their usage frequency. Each cached item maintains a usage counter that increments upon access. When the cache reaches its capacity limit, it removes the item with the lowest usage count to free up space.
Note: This project has been updated to run on Linux using NUnit for testing and Visual Studio Code as the development environment.
Install via NuGet Package Manager:
Install-Package LFUCache -Version 1.0.2
ICache<string, string> cache = new LfuCache<string, string>(1000);
cache.Add("name", "Helene");
cache.Add("surname", "Stuart");
var name = cache.Get("name");The LfuCache class implements the ICache interface:
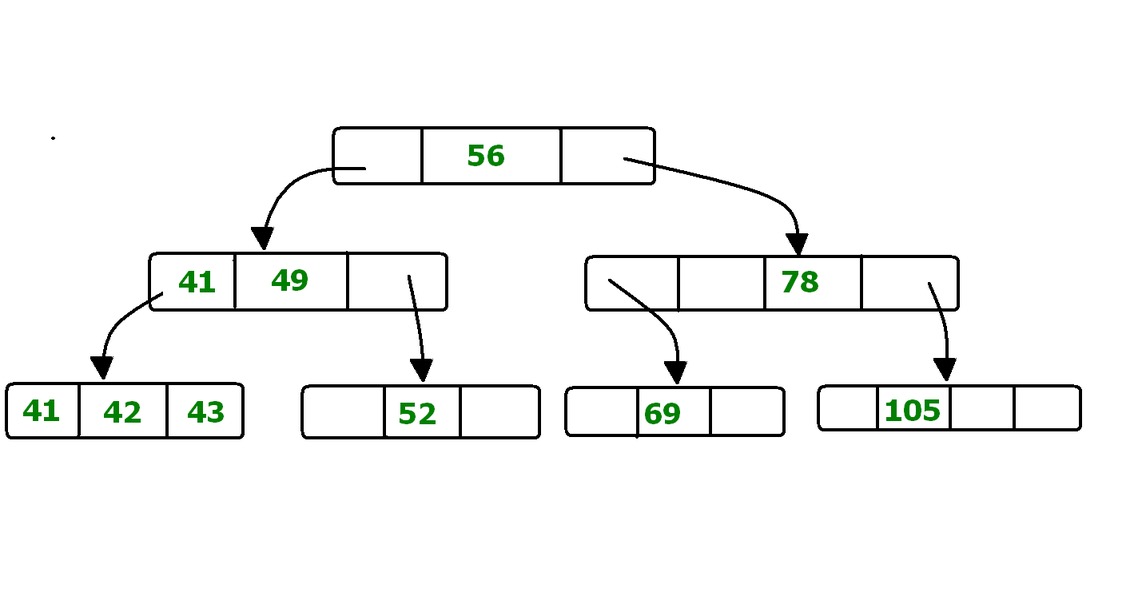
The implementation uses a hybrid data structure combining:
- A
SortedListwhere the key is the usage count - A
LinkedListas the value, containing all elements with the same usage count
This structure is organized as a binary tree of linked lists, enabling O(log n) time complexity for both Add and Get operations.
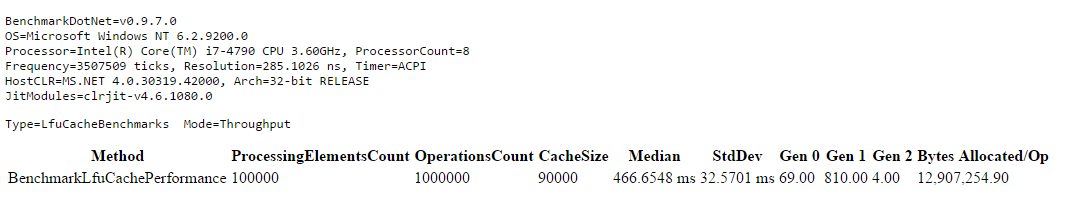
The cache demonstrates impressive performance:
- 1,000,000 add/get operations
- Cache size: 90,000 items
- Dataset size: 100,000 elements
- Execution time: 466ms
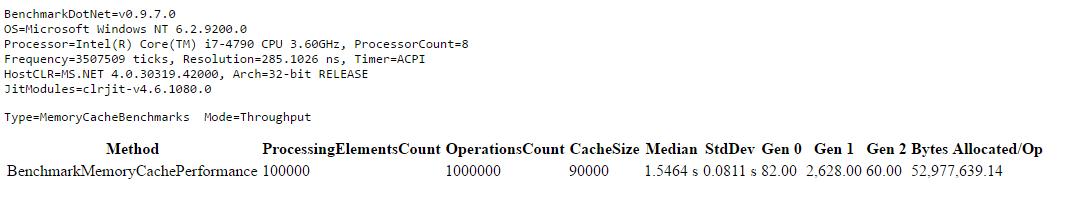
Compared to .NET Framework's MemoryCache, this implementation:
- Executes faster
- Uses less memory
- Maintains consistent performance
The benchmarks:
- Use randomly generated Add/Get operation sequences in
BitArray - Process elements from a fixed-size list
- Are conducted using BenchmarkDotNet
Unit tests are written using the NUnit framework with comprehensive code coverage tracked through Azure Pipeline.